As the construction industry increasingly emphasizes efficiency and safety, automation technologies are transforming the way projects are executed. These innovations are not only driving significant productivity gains but also addressing critical labor shortages and improving overall project quality. This article delves into the multifaceted role of automation in construction, highlighting its numerous advantages, such as precision and time savings, while also exploring the challenges of adoption. Additionally, it examines real-world applications, showcasing how automated systems and machinery are revolutionizing workflows and setting new benchmarks for the industry’s future.
Table of Contents

What is automation in construction?
Automation in construction refers to the integration of advanced technologies to perform tasks traditionally managed by human labor, aiming to revolutionize the industry. This encompasses a wide range of applications, including autonomous machinery such as excavators and bulldozers executing on-site physical tasks with precision, as well as sophisticated software systems that streamline project planning, scheduling, and execution. By minimizing manual intervention, automation enhances operational efficiency, reduces the likelihood of errors, and significantly improves safety on construction sites by greatly reducing near miss events, creating a more productive, reliable, and safer working environment for all stakeholders.
Key Technologies Driving Automation in Construction Machinery.
The heavy equipment and machinery sector is undergoing a transformative shift as automation technologies become integral to improving efficiency, safety, and productivity. Here’s a detailed look at the key technologies shaping the future of automation in the industry:
1. Robotics
Robotics is reshaping the construction industry by automating complex, labor-intensive tasks and redefining how heavy equipment operates. This cutting-edge technology enhances efficiency, reduces errors, and improves safety in environments that often present significant risks. Below, we explore two key robotic innovations transforming the field:
- Robotic Arms: These advanced systems are now integral to tasks requiring precision, such as masonry, assembly, and material handling. Robotic arms can perform repetitive actions with unmatched accuracy, reducing the margin of error while boosting overall productivity. By working continuously without fatigue, they streamline operations and significantly cut down project timelines. Many of these arms are integrated with AI-powered controls, allowing them to adapt to real-time conditions and make autonomous decisions for optimized performance.
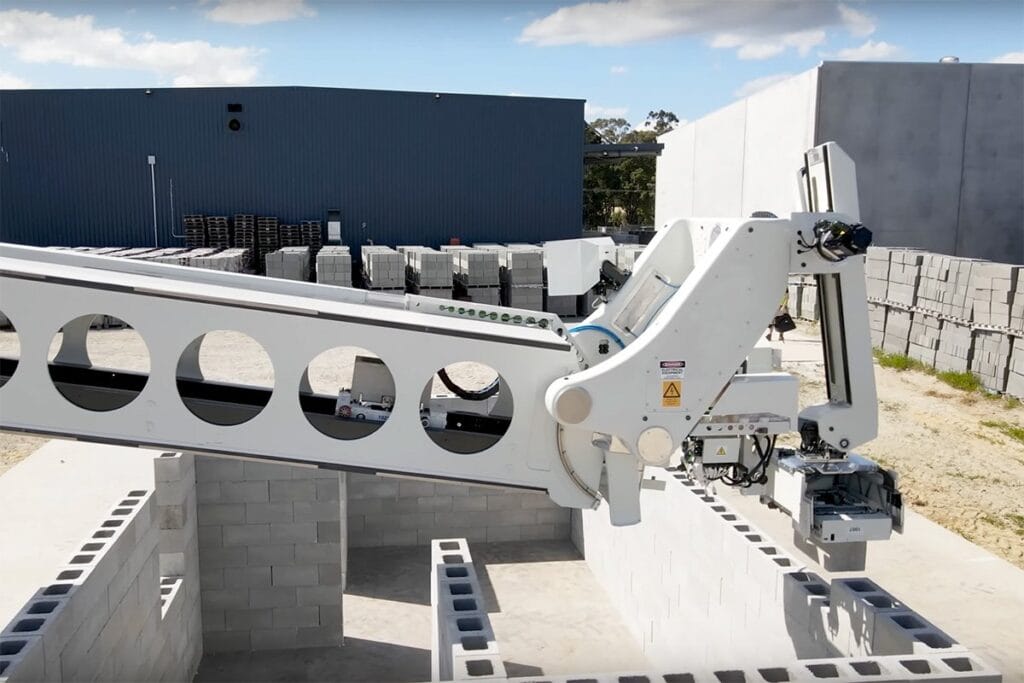

- Drones: Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are no longer just tools for surveying; they are indispensable in material transport, safety inspections, and site monitoring. Equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors, drones provide precise data for creating detailed topographic maps and assessing site conditions. Their ability to access hard-to-reach or hazardous areas minimizes risks for workers while accelerating project planning and execution. Additionally, drones are increasingly used to monitor equipment performance and track construction progress in real-time, ensuring projects stay on schedule.
Robotics in construction is paving the way for smarter, safer, and more efficient heavy equipment operations. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more groundbreaking applications in the near future.
2. Building Information Modelling (BIM)
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is revolutionizing the way construction projects are planned, executed, and managed. This technology bridges the gap between design and construction workflows by creating detailed digital representations of physical structures. By offering a holistic view of the project lifecycle, BIM empowers construction teams to achieve greater precision, efficiency, and collaboration. Here’s how BIM is reshaping the heavy equipment and construction industries:
- Enhanced Planning: BIM allows teams to visualize entire projects in a highly detailed 3D environment. This enables better planning, from site preparation to resource allocation, ensuring that potential challenges are addressed well before construction begins. For example, teams can simulate the placement of heavy machinery on-site, reducing inefficiencies and preventing costly delays.
- Collaboration: Integrating data from architects, engineers, contractors, and heavy equipment operators, BIM fosters seamless collaboration among stakeholders. Everyone involved has access to the same up-to-date information, minimizing errors caused by miscommunication or outdated plans. This shared platform ensures that teams work cohesively, optimizing project outcomes.
- Efficiency Gains: With simulation and predictive modeling capabilities, BIM identifies potential issues like structural conflicts or workflow inefficiencies early in the design process. These insights save time and resources during construction by enabling adjustments before any physical work begins. Heavy equipment operators benefit directly, as BIM provides precise instructions on excavation, grading, or material placement, reducing rework and improving productivity.
BIM is not just a tool but a transformative force that is redefining how projects are approached and completed in 2025. By integrating this technology, construction firms can streamline their operations and enhance the overall efficiency of heavy equipment utilization.
3. Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing the construction industry by connecting equipment, sensors, and systems to create smarter, more efficient job sites. This cutting-edge technology enables real-time communication and data sharing, fostering improved decision-making, operational efficiency, and safety. Here are the key ways IoT is transforming heavy equipment and construction processes:
- Real-Time Monitoring: IoT devices collect and transmit data on equipment performance, fuel consumption, and site conditions. Operators and managers can access this data through dashboards, allowing them to monitor operations in real-time. For instance, if a machine is operating outside optimal parameters, the system can immediately flag the issue, enabling swift corrective action and minimizing potential disruptions.
- Predictive Maintenance: One of the most impactful applications of IoT is its ability to prevent costly equipment failures. Sensors embedded in machinery continuously gather data on components like engine temperature, hydraulic pressure, and vibration patterns. By analyzing this data, the system can predict when parts are likely to fail, prompting timely maintenance and reducing downtime significantly.
- Safety Enhancements: IoT technology improves safety by tracking the location of workers and equipment on the job site. Proximity sensors and geofencing help prevent accidents by alerting operators when workers are too close to machinery. Additionally, IoT systems can monitor environmental conditions like temperature, noise, and air quality, ensuring a safer work environment for everyone on-site.
With IoT, the construction industry is moving toward a future where job sites are more connected, efficient, and secure, underscoring the transformative potential of this technology in 2025 and beyond.
4. 3D Printing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is revolutionizing the heavy equipment industry by offering innovative solutions for component fabrication and repair. This technology is transforming traditional manufacturing processes, providing efficiency, cost savings, and environmental benefits. Below are key ways 3D printing is impacting heavy equipment in construction:
- Quick Prototyping: One of the most significant advantages of 3D printing is its ability to rapidly produce prototypes for machinery parts and components. Engineers can test and refine designs in a fraction of the time it would take using conventional methods, accelerating the development of advanced heavy equipment. This speed fosters innovation by allowing manufacturers to experiment with new features and technologies without lengthy delays.
- On-Demand Manufacturing: Supply chain disruptions can cause costly delays in construction projects. 3D printing mitigates this issue by enabling the fabrication of parts on-site or as needed. This approach reduces reliance on large inventories, lowers storage costs, and ensures machinery downtime is minimized, keeping operations running smoothly.
- Customization and Repair: With 3D printing, customized parts can be produced to meet specific requirements, accommodating unique machinery needs or project demands. Additionally, damaged or obsolete parts can be repaired or recreated quickly, extending the lifespan of equipment and reducing replacement costs.
- Sustainability: By using only the material required for each part, 3D printing significantly reduces waste compared to traditional manufacturing methods. This aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainability in the construction industry, making it a greener choice for producing heavy equipment components.
The adoption of 3D printing in construction is not just about improving efficiency—it’s about reshaping how the industry approaches innovation and problem-solving. As this technology continues to advance, its impact on heavy equipment manufacturing and maintenance will only grow, making it a critical tool for the future of construction.
5. Telematics Technology
In the ever-evolving world of construction, telematics technology has become a game-changer, bridging the gap between machinery and data-driven decision-making. By providing actionable insights into equipment operations, telematics empowers construction companies to enhance productivity, efficiency, and safety. Below are the keyways telematics technology is transforming heavy equipment:

- Remote Monitoring: Modern telematics systems collect and transmit critical data, including machine usage, fuel consumption, engine health, and hydraulic pressure. With real-time updates accessible from anywhere, operators and managers can oversee equipment performance and swiftly address issues, even on remote job sites.
- Predictive Analytics: Telematics leverages historical and live data to identify patterns and predict potential equipment failures. This enables proactive maintenance schedules, reducing the likelihood of costly breakdowns and unplanned downtime, while extending the lifespan of machinery.
- Enhanced Fleet Management: For companies managing multiple machines across different locations, telematics provides a centralized platform to track equipment status, location, and usage. This ensures optimized fleet utilization, improved job-site coordination, and reduced operational expenses.
- Safety Improvements: With telematics, safety is no longer an afterthought. The technology issues alerts and diagnostics to ensure machinery operates within safe parameters, helping to minimize the risk of accidents and protecting operators and assets alike.
Automation in heavy equipment and machinery is advancing rapidly, driven by technologies such as robotics, BIM, IoT, telematics, and 3D printing. These innovations not only enhance productivity and efficiency but also improve safety and sustainability. As these technologies continue to evolve, they will define the future of heavy machinery, empowering industries to achieve greater operational excellence.
Benefits of Automation in Construction Machinery.
The incorporation of automation into construction workflows provides numerous substantial benefits, reshaping how projects are executed and delivering advantages across safety, efficiency, cost management, and quality assurance.
- Enhanced productivity and operational efficiency: Automation dramatically accelerates repetitive processes like material handling, excavation, and component assembly. Technologies such as robotic bricklaying systems can lay bricks with incredible precision and speed, surpassing the output of human labor. Autonomous bulldozers and excavators also streamline large-scale earthmoving tasks by working tirelessly and efficiently. These advancements allow construction teams to complete projects faster, meet tight deadlines, and handle multiple projects simultaneously without compromising on quality.
- Improved worker safety: Automating high-risk tasks minimizes human exposure to dangerous environments. For example, robots can operate in confined spaces or at elevated heights where manual work would pose significant risks. Automated equipment also reduces the need for workers to handle heavy materials manually, lowering the likelihood of injuries. Moreover, advanced systems equipped with real-time monitoring sensors provide instant alerts about unsafe conditions such as unstable structures or harmful gas leaks, enabling proactive interventions and fostering a safer work environment.
- Cost efficiency and minimized operational downtime: By optimizing workflows, automation reduces labor-intensive tasks, helping to cut costs associated with manual labor and project delays. Automated systems like concrete batching plants ensure precise material measurements, eliminating waste and rework. Predictive maintenance tools integrated into machinery detect potential issues before they escalate, preventing unexpected breakdowns and costly downtime. Over time, these efficiencies result in significant savings for construction companies.
- Precision and enhanced project integrity: Automation enhances accuracy in measurements, material application, and component placement, leading to fewer defects and higher build quality. Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and LiDAR technology perform ongoing site inspections, ensuring compliance with design specifications and highlighting inconsistencies in real time. This level of precision reduces errors, minimizes costly rework, and boosts overall project integrity.
Automation is not just improving individual aspects of construction but transforming the entire industry, setting new standards for productivity, safety, and quality in 2025 and beyond.
Challenges Faced in Automating Construction Machinery
While automation in construction offers significant advantages, its implementation is not without challenges:
- Initial capital expenditure and deployment costs: The upfront investment required for procuring automated systems and training staff can be significant, creating an entry barrier for many firms.
- Workforce training and skill enhancement: As automation technology advances, the demand for a skilled workforce capable of operating advanced machinery and
analysing data from automated systems continues to grow. - Technical constraints and system reliability: Automated systems must perform
consistently under diverse site conditions, any malfunction could result in costly
project delays or potential safety risks. - Seamless integration with existing processes and legacy infrastructure: Many
construction companies still depend on conventional practices, incorporating new
automated systems into established workflows can be complex and necessitate
substantial modifications.

Case Study: Real-world example of a construction company utilizing automation effectively.
A notable illustration of effective automation in construction is demonstrated by Factory_OS, headquartered in Vallejo, California, which leverages modular construction methods. Specializing in the production of multifamily housing units, the company employs an intelligent manufacturing model that prioritizes efficiency through automated processes. By incorporating advanced production techniques, Factory_OS delivers high-quality modular homes at a faster pace than traditional construction while minimizing material waste. The use of QR codes for real-time part tracking throughout the assembly line ensures accuracy and consistency. In a significant project focused on affordable housing, Factory_OS achieved substantial reductions in construction timelines compared to conventional on-site building practices.
Key takeaways from this case study include:
- The importance of leveraging technology to improve efficiency.
- The potential for modular construction to address housing shortages effectively.
- The necessity for collaboration between design, fabrication, and assembly teams to optimize outcomes.
Conclusion
The future of automation in construction is bright, with technology driving improved productivity, safety, and quality. While challenges exist, investing in workforce training and seamless system integration ensures companies remain competitive and efficient. By embracing automation, industry leaders can unlock transformative advancements that revolutionize project execution and redefine construction processes from planning to completion.

Ningo, founder of Big Machines Today, is a passionate writer and content creator specializing in heavy-duty machinery. Focused on delivering industry insights and trends, Ningo crafts engaging content for professionals. Open to free collaborations on blogs or social media articles, Ningo invites you to connect and explore the Big Machines Today Blog for valuable updates.













I’m really learning a lot
Thank you for your kind words! We’re thrilled to hear that you’re finding our content valuable. If you have any specific topics you’d like us to cover or questions about heavy equipment, feel free to let us know.!